
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Tuesday Dec 2 2025 10:00

15 min

What is CFD trading strategy: Contract for Difference (CFD) trading has emerged as one of the most popular methods for trading various financial instruments.
CFD trading guide: CFDs allow traders to speculate on price movements of assets without owning the underlying assets. This flexibility, along with the potential for high returns, makes CFD trading an attractive option for both beginners and experienced traders alike. This flexibility, along with the potential for high returns, makes CFD trading an attractive option for both beginners and experienced traders alike.
CFDs are derivatives that enable traders to profit from the rising or falling prices of assets such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices. When engaging in CFD trading, the trader enters a contract with a broker to exchange the difference in the price of an asset between the opening and closing of the contract. This allows traders to leverage their investments, potentially amplifying their returns (and risks).
Despite the advantages, CFD trading carries significant risks:

To improve your CFD trading success, it’s essential to understand market dynamics and factors that influence price movements.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial health and market conditions to make trading decisions. Key elements include:
Economic Indicators: GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, and inflation rates can dictate overall market sentiment.
Company Financial Statements: Analyzing income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements can provide insights into a company’s performance.
News Events: Markets react sharply to news regarding earnings reports, acquisitions, and other significant events.
Technical Analysis
In contrast to fundamental analysis, technical analysis focuses on historical price movements and chart patterns. Understanding charts and technical indicators can enhance trading strategies:
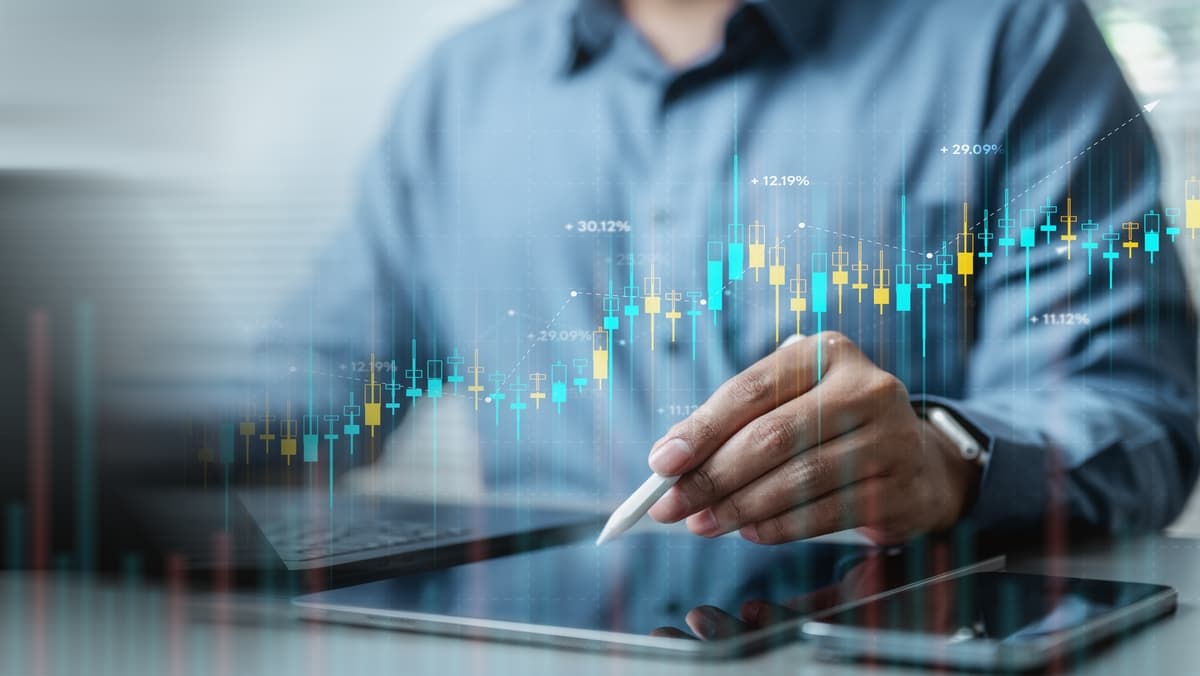
Charts: Line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts provide different perspectives on price movements.
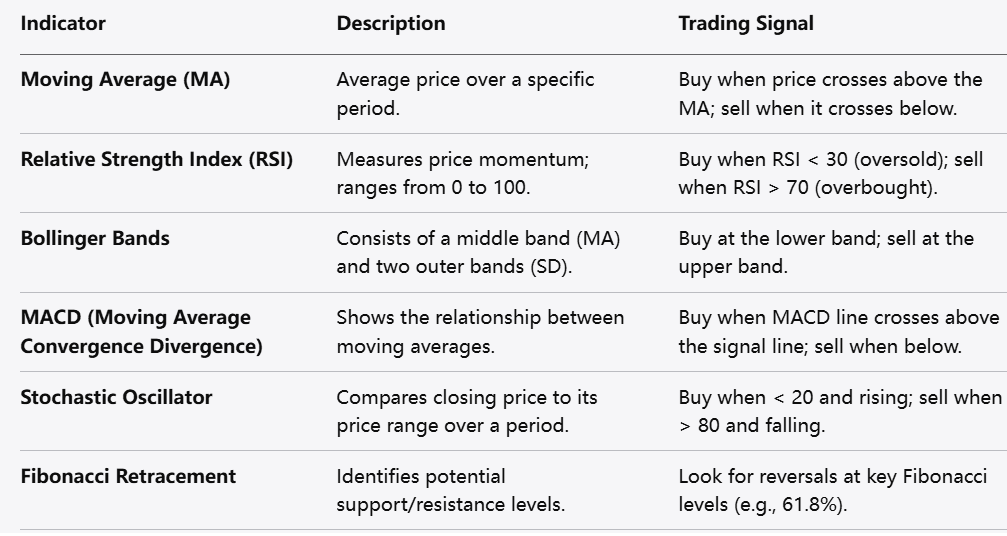
Indicators: Tools like moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and RSI help traders make informed decisions by filtering out noise and highlighting trends.
For beginners looking to start trading CFDs, understanding effective strategies is crucial. Here are some profitable CFD trading strategies to consider:
1. News Trading
News trading involves reacting quickly to news releases that can impact asset prices. Economic indicators, earnings reports, and geopolitical events significantly affect market sentiment. By staying informed and analyzing the news, traders can make quick decisions to capitalize on price movements.
How to Implement: Monitor economic calendars for important news releases. Identify the market sentiment and determine whether to go long or short based on expectations. Consider using a demo account to practice reacting to different news scenarios.
2. Trading with Technical Analysis Indicators
Technical analysis involves using charts and indicators to analyze price movements and identify potential trading opportunities. Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
How to Implement: Familiarize yourself with different indicators and their applications. Use them to identify trends, overbought or oversold conditions, and entry/exit points. For example, combine moving averages with RSI to determine when an asset may be reversing.
3. Price Action Trading
Price action trading is the practice of making trading decisions based on the historical price movement of an asset without relying on indicators. Traders study candlestick patterns, support and resistance levels, and market structure to make informed decisions.
How to Implement: Learn to read price charts and recognize patterns. Look for key support and resistance levels to identify potential reversals or breakouts. Practice price action strategies in a demo account to develop your skills.
4. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading involves entering a position when the price breaks through a significant support or resistance level. This strategy assumes that once the price breaks through a level, it will continue in that direction.
How to Implement: Identify key levels of support and resistance. When the price breaks through a level, enter a trade in the direction of the breakout. Use stop-loss orders to manage risk. Monitoring volume can also provide additional confirmation of a breakout.
5. Hedging
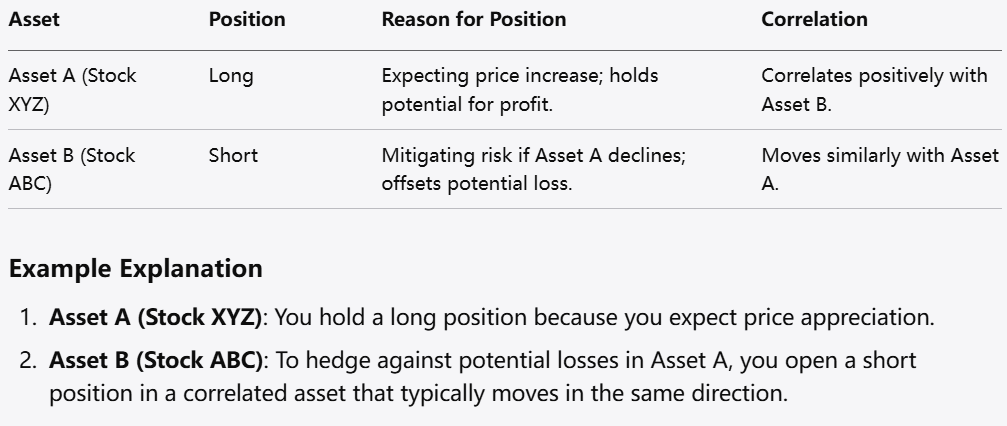
Hedging is a strategy used to protect against potential losses by taking a position in a related asset. For CFD traders, this might involve opening a short position on a security while holding a long position on a similar asset to offset potential losses.
How to Implement: Determine correlations between assets. If you hold a long position in one CFD, take a short position in a correlated asset to mitigate potential losses. This strategy can help guard against market downturns.
6. Position Trading
Position trading involves holding a position for an extended period, typically weeks or months. This strategy is based on fundamental analysis and the belief that the market will eventually move in your favor.
How to Implement: Conduct thorough fundamental analysis and identify long-term trends. Use wider stop-loss orders to accommodate for market fluctuations. Be prepared to hold positions through short-term volatility.
7. Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling assets within the same trading day, often capitalizing on short-term price movements. This strategy requires quick decision-making and effective risk management.
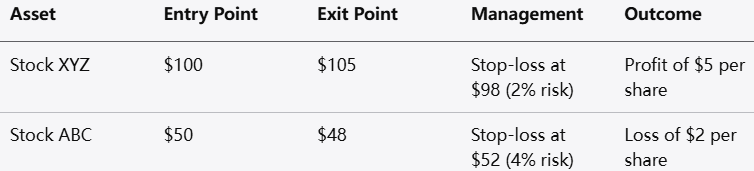
How to Implement: Develop a solid trading plan that includes entry and exit points. Use technical analysis to identify potential trades and manage your risk carefully. Limit your trades to a few high-probability setups to avoid overtrading.
8. Swing Trading
Swing trading aims to capture short- to medium-term price movements by holding positions for several days or weeks. This approach allows traders to take advantage of price "swings" in the market.
How to Implement: Identify swing points on charts and use technical analysis to make trading decisions. Focus on stocks or assets with high volatility for better price swings. Managing your trades with appropriate stop-loss orders can help minimize risks.
No trading strategy is complete without a well-structured risk management plan. Managing risk is crucial to long-term success in CFD trading.
Understanding Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The risk-to-reward ratio helps traders define their potential profit relative to the potential loss of a trade. A common guideline is to target a risk-to-reward ratio of at least 1:2, meaning you aim to make twice what you risk.
How to Calculate: If you risk a certain amount to gain a certain amount, you can easily determine if the trade is worth taking. For instance, risking 10 units to gain 20 units adheres to the 1:2 ratio.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Using stop-loss and take-profit orders is vital for protecting your trading capital. A stop-loss order automatically closes a position at a predetermined loss level, while a take-profit order captures profits at a specific price point.
How to Implement: Identify support and resistance levels when setting stop-loss orders. Ensure that your take-profit levels are in line with your risk-to-reward ratio.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how much capital you allocate to each trade, directly affecting your risk exposure. Proper position sizing can help prevent significant losses and ensure a sustainable trading approach.
How to Calculate: Use a percentage of your total trading account balance to determine position size. A common recommendation is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total balance on a single trade.
Trading Psychology
Successful CFD trading extends beyond strategy and analysis; it also requires strong trading psychology. Traders must cultivate the right mindset to navigate the complexities of the market.
Emotional Discipline
Emotions can sway traders’ decisions and lead to impulsive trades or massive losses. Developing emotional discipline involves creating a clear trading plan and sticking to it.
How to Cultivate: Establish rules and guidelines for entering and exiting trades. Acknowledge emotions but make decisions based on logic and strategy rather than feelings.
Avoiding Overtrading
Overtrading can erode profits and increase transaction costs. Traders may be tempted to enter multiple trades in search of quick profits, leading to significant losses.
How to Combat: Set a maximum number of trades for each day or week. Focus on quality over quantity by only taking high-probability trades.
Learning from Losses
Every trader will experience losses. The key is to analyze losing trades to understand what went wrong, allowing for better decision-making in the future.
How to Reflect: Maintain a trading journal to document each trade, including your thought process, emotions, and outcomes. Reviewing this information can provide valuable insights for improvement.
Building a Trading Plan
Creating a trading plan is critical for any trader, especially beginners. A comprehensive trading plan should include:
Objectives and Goals
Define your trading objectives clearly. Specify the types of assets you want to trade, your risk tolerance, and your financial goals. Establish short-term and long-term goals to track your progress.
Criteria for Trade Entry and Exit
Outline the conditions necessary for entering and exiting trades. This should encompass technical indicators, chart patterns, and fundamental factors. Clear criteria will help you make objective decisions.
Risk Management Strategy
Incorporate your risk management approach, including stop-loss levels and position sizing. Ensure that your plan allows for sustainable trading practices that protect your capital.
Continuous Education
The financial markets are ever-evolving, and continuous education is crucial. Stay updated with market trends, new strategies, and changes in regulations.
How to Continue Learning: Read books, attend webinars, and follow experienced traders. Joining trading communities can facilitate knowledge exchange and support.

CFD trading offers a variety of strategies that can be employed based on individual trading styles, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Beginners should take the time to understand each strategy and develop a solid trading plan. While the potential for profit is significant, it’s essential to remember that trading CFDs carries risks that must be managed wisely.
For anyone entering the world of CFD trading, continuous learning and practice will ultimately lead to improved trading performance and confidence in making decisions. As traders become more familiar with the markets and their strategies, they can adapt their approaches to maximize their potential for profitability.
By combining effective strategies with proper risk management and continuous education, beginner traders can set the foundation for successful CFD trading and navigate the complexities of the financial markets with greater confidence.
Looking to trade CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
To support your journey in CFD trading, consider exploring the following resources:
Books: Look for books on trading strategies, technical analysis, and psychology. Titles like "Trading in the Zone" by Mark Douglas can enhance your understanding of trading psychology.
Online Courses: Many trading platforms offer online courses that cover everything from the basics of CFD trading to advanced strategies.
Webinars and Seminars: Attend live or recorded sessions hosted by experienced traders or industry experts to gain insights and tips.
Trading Forums and Communities: Joining online communities can provide additional support, insights, and real-time market discussions.
Remember, the journey to becoming a successful CFD trader involves continuous learning, practice, and dedication. Stay disciplined and focused on your trading goals, and you can navigate the complexities of the market effectively.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.