
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Wednesday Nov 26 2025 09:26

10 min

What are technical indicators: Contract for Difference (CFD) trading has become increasingly popular among retail and professional traders due to its flexibility, leverage, and ability to profit from both rising and falling markets.
CFD Trading Basics: However, CFD trading involves significant risk, and success often depends on a trader's ability to analyze market conditions effectively. One of the most essential tools in a trader’s arsenal is technical indicators.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into what technical indicators are, how they work, and how you can use them strategically in CFD trading to improve your chances of success. This guide will cover everything from the basics to advanced concepts, providing detailed insights for traders at every level.
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on the price, volume, or open interest of a security or contract. They are used to forecast future price movements by analyzing past market data. In CFD trading, technical indicators help traders identify trends, momentum, volatility, and potential reversal points—critical factors to making informed trading decisions.
Unlike fundamental analysis, which examines economic and financial factors, technical analysis relies purely on price action and market data. The core belief behind technical indicators is that all market information is already reflected in the price, and price movements tend to repeat over time due to market psychology.
CFDs allow traders to speculate on the price movements of various underlying assets, including stocks, commodities, forex, and indices without owning the assets themselves. Because CFDs are leveraged products, small price movements can lead to significant profits or losses.
Using technical indicators in CFD trading helps traders:
In essence, technical indicators serve as a guide to improve trading discipline and reduce emotional decision-making.
Technical indicators can be broadly classified into four categories:
Trend Indicators
These indicators help traders identify the direction and strength of a market trend. They are most effective in trending markets and can signal whether to enter a trade with the trend or avoid counter-trend trades.
Momentum Indicators
Momentum indicators measure the speed and magnitude of price changes. They can signal overbought or oversold conditions, helping traders anticipate potential reversals.
Volatility Indicators
Volatility indicators assess the degree of price fluctuation over a period. High volatility often means larger price swings, while low volatility indicates consolidation phases.
Volume Indicators
Volume indicators analyze the amount of trading activity, offering clues about the strength behind price movements.
Moving Averages (MA)
Moving Averages smooth out price data to create a single flowing line, making it easier to identify the direction of the trend. The two most common types are:
Simple Moving Average (SMA): The average price over a set period.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information.
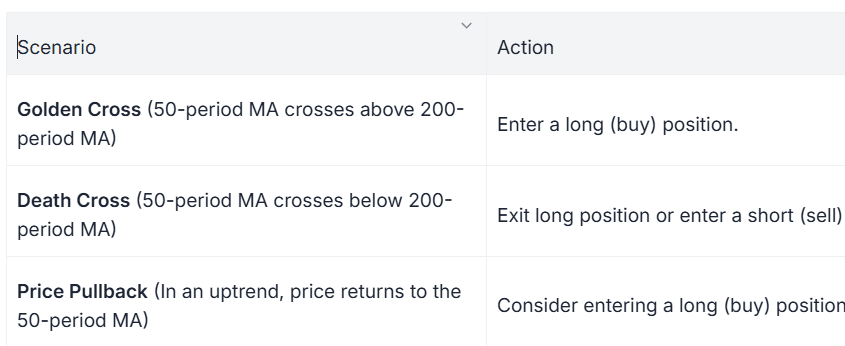
How to Use:
Traders often use moving averages to identify trend direction and potential support/resistance levels. A popular strategy involves the crossover of two moving averages (e.g., 50-period and 200-period) to generate buy or sell signals.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
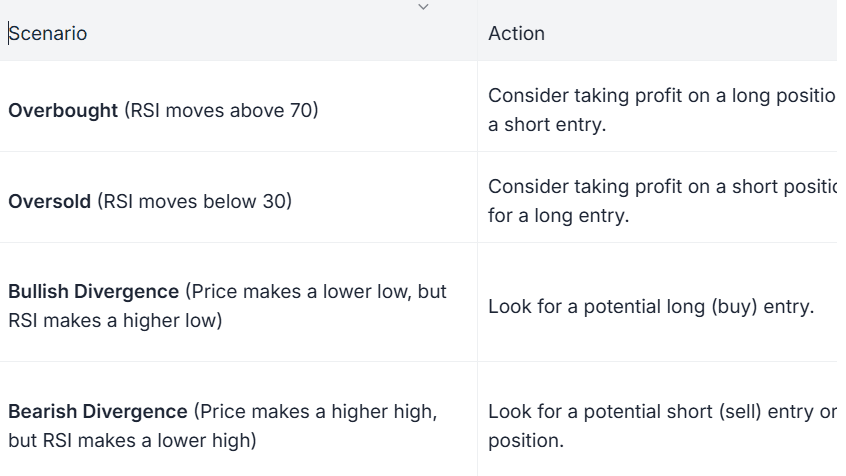
RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements on a scale of 0 to 100.
Readings above 70 typically indicate overbought conditions (potential sell signal).
Readings below 30 indicate oversold conditions (potential buy signal).
How to Use:
RSI helps traders identify potential reversal points when the market is stretched beyond typical limits.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
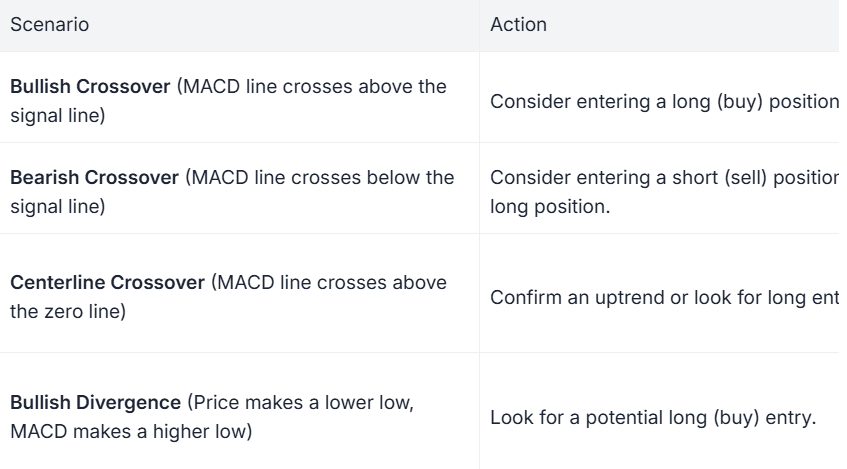
MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It consists of the MACD line, signal line, and histogram.
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it generates a bullish buy signal.
When it crosses below, it generates a bearish sell signal.
How to Use:
MACD is excellent for spotting trend changes and momentum shifts.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (usually a 20-period SMA) and two outer bands that represent standard deviations away from the middle band.
When price touches the upper band, the market may be overbought.
When price touches the lower band, the market may be oversold.
How to Use:
Bollinger Bands help in identifying volatility and potential reversal points.
Stochastic Oscillator
This momentum indicator compares a particular closing price to a range of its prices over a certain period. It ranges from 0 to 100.
Readings above 80 indicate overbought levels.
Readings below 20 indicate oversold levels.
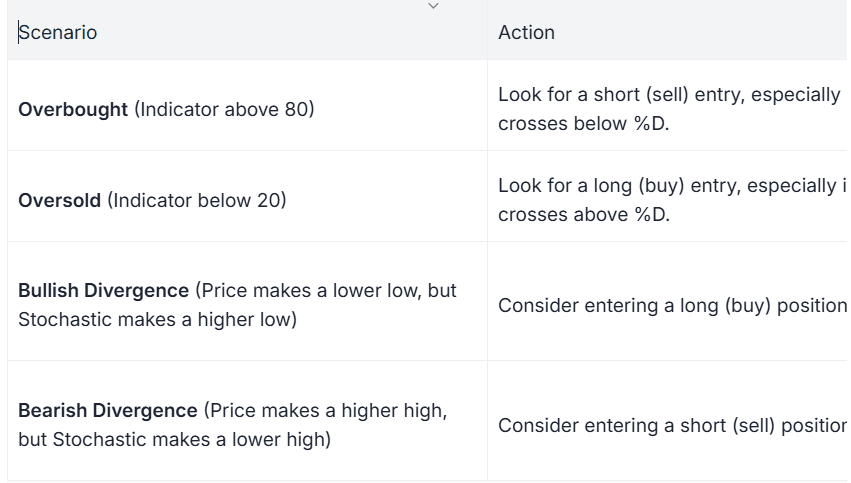
How to Use:
Stochastics can help find entry points in trending or ranging markets by signaling when the market is potentially reversing.
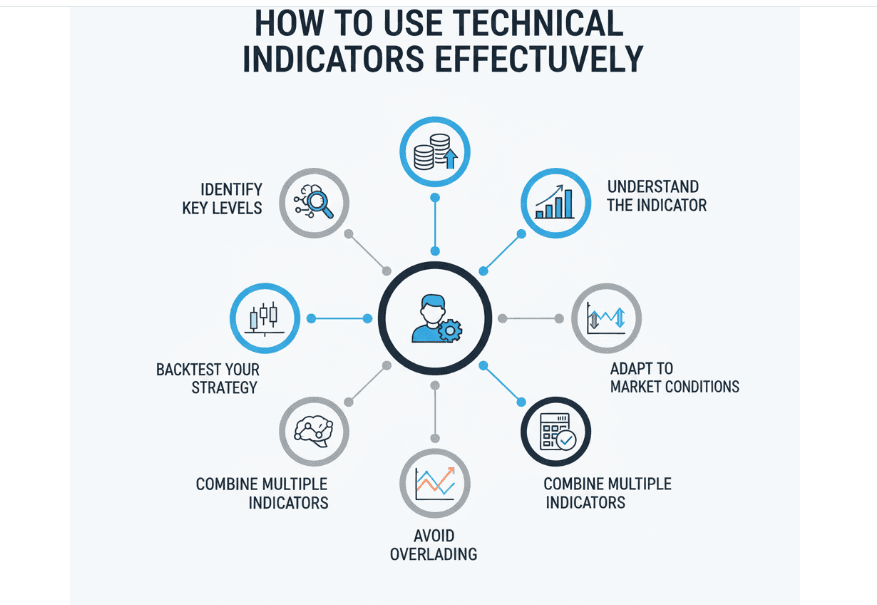
Combining Indicators
Using multiple indicators that measure different market aspects (trend, momentum, volatility) can provide a more comprehensive market view. For example, combining a trend indicator with a momentum indicator can confirm trade signals and reduce false entries.
Avoiding Indicator Overload
Using too many indicators can create confusion and contradicting signals, known as “analysis paralysis.” Stick to a few reliable indicators that complement each other.
Setting Indicator Parameters
Indicators have default settings, but adjusting these based on the asset’s volatility and trading timeframe can improve accuracy. For example, short-term traders may use shorter moving averages, while long-term traders opt for longer periods.
Trend Following Strategies
This approach involves trading in the direction of the prevailing trend. For example:
Use moving average crossovers to confirm trend direction.
Enter long positions during uptrends and short positions during downtrends.
Use RSI or Stochastic to avoid entering trades when the market is overbought or oversold.
Reversal Strategies
Reversal strategies aim to identify when a trend is losing momentum and about to change direction.
Use RSI or Stochastic to spot overbought or oversold conditions.
Look for divergence between price and momentum indicators (e.g., price makes new highs but RSI doesn’t).
Confirm with candlestick patterns or support/resistance zones.
Breakout Strategies
Breakouts occur when price moves beyond a defined support/resistance level or a consolidation range.
Use Bollinger Bands or volatility indicators to anticipate breakouts.
Confirm with volume spikes.
Enter trades in the breakout direction, placing stop-loss orders just outside the breakout zone.
Relying on a Single Indicator: No indicator is perfect; always use confirmation tools.
Ignoring Market Context: Indicators work best in specific market conditions; a trend indicator may fail in a sideways market.
Overfitting Parameters: Tweaking settings excessively to fit historical data can lead to poor real-time performance.
Neglecting Risk Management: Overconfidence in indicators can lead to ignoring stop-losses and risking too much capital.
Technical indicators can help in setting stop-loss and take-profit levels by identifying logical exit points based on support and resistance or volatility bands.
However, risk management should always be a priority:
Decide how much capital you’re willing to risk per trade.
Use position sizing techniques to align with your risk tolerance.
Always have a stop-loss in place to protect your account.
Don’t let indicators override sound money management principles.
Technical indicators are invaluable tools in CFD trading, providing insights into market trends, momentum, volatility, and volume. When used properly, they can enhance trading decisions and increase the likelihood of profitable trades.
However, it is crucial to understand that indicators are not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with other analysis methods and strict risk management. Mastery of technical indicators requires practice, patience, and a clear trading plan.
By combining knowledge of different indicators, understanding market context, and maintaining disciplined risk control, traders can harness the power of technical indicators to navigate the complexities of CFD markets successfully.
Looking to trade CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.