
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Tuesday Jan 20 2026 10:15

17 min

Futures CFDs trading: Futures trading has become a popular option for traders looking to invest in various assets without owning them outright.
Beginner's guide to CFD trading: Utilizing Contracts for Difference (CFDs) on futures can further enhance trading opportunities by allowing for speculation on price movements. This article offers an in-depth exploration of futures trading, how it works, and strategies for engaging in this market. Additionally, we'll highlight why Markets.com is a strong choice for futures CFD trading.
Futures are financial contracts obligating the buyer to purchase, and the seller to sell, a particular asset at a predetermined future date and price. These contracts can be based on a variety of assets, including commodities, indices, and currencies. Futures trading originated in the agricultural sector, where farmers would hedge against price fluctuations by locking in prices for their crops before harvest.
Key Features of Futures Contracts
Standardized Contracts: Futures contracts are standardized in terms of quantity, expiration date, and quality (where applicable), making them easily tradable on exchanges.
Commodity Futures: These include contracts for physical goods such as oil, gold, wheat, and cattle. Commodity futures are highly influenced by supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and economic indicators.
Financial Futures: This category includes contracts for financial instruments such as stock indices, interest rates, and currencies. Financial futures are often used to hedge financial portfolios against market fluctuations.
Index Futures: Contracts based on stock market indices, such as the S&P 500 or Dow Jones, allowing traders to speculate on the overall movement of the stock market.
Currency Futures: Futures contracts based on currency pairs, allowing traders to take positions on future exchange rate movements.

Futures Contracts for Difference (CFDs) allow traders to speculate on the price movement of futures contracts without having to own the underlying asset. Instead of buying the actual futures contract, traders enter into an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in the contract's price from the time of opening to the time of closing.
Characteristics of Futures CFDs
No Ownership of Underlying Asset: Traders do not take ownership of the underlying asset, which can simplify the trading process.
Flexible Trading Options: Futures CFDs can often be traded with more flexible options than traditional futures contracts, including shorter timeframes and varied contract sizes.
Leverage: Like traditional futures trading, futures CFDs are often traded with leverage, allowing for greater exposure with a smaller capital investment.
No Expiration Dates: Futures CFDs may not have strict expiration dates, allowing traders to maintain positions for as long as they choose, depending on the broker's terms.
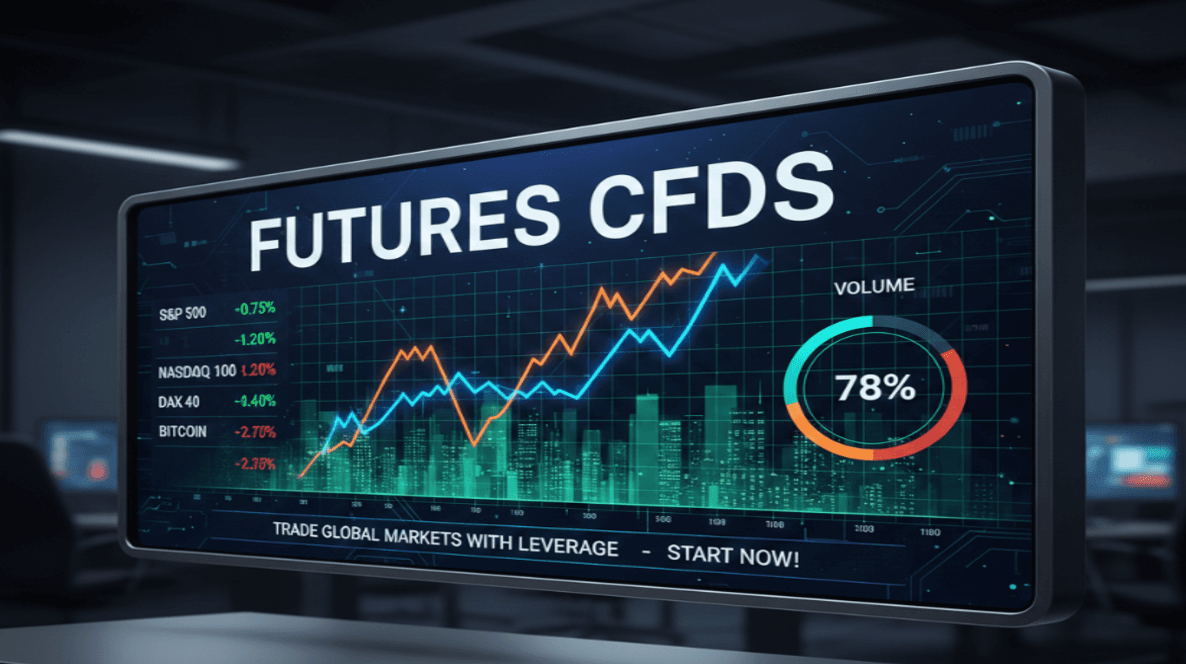
The Mechanics of Futures Trading
Opening a Trade: To enter a futures trade, the trader places an order with a broker. The trade can be initiated either as a long position (buy) or a short position (sell), depending on the trader's expectations of market movements.
Margin Trading: Traders are required to deposit an initial margin with the broker to open a position. This margin is expressed as a percentage of the contract's total value.
Daily Settlement: Futures are marked to market daily, meaning that profits and losses are calculated and settled at the end of each trading day, affecting the margin balance.
Closing a Position: Traders can close their positions at any time before the expiration of the contract. The difference between the opening price and closing price will determine profit or loss.
S
ample Trading Process in Futures CFDs
Open a Trading Account: The first step is to select a reputable broker like Markets.com and open a trading account.
Deposit Margin: Fund the account by depositing the required margin amount to trade your desired futures contract.
Choose Your Contract: Decide which futures contract to trade based on research, analysis, and personal preference.
Place an Order: Execute a buy or sell order. You’ll need to specify the quantity and type of order (market, limit, etc.).
Monitor Your Position: Keep an eye on market movements and any relevant events that may affect your position.
Close Your Position: When you're ready to take profits or stop losses, close your position, thereby realizing the price difference.
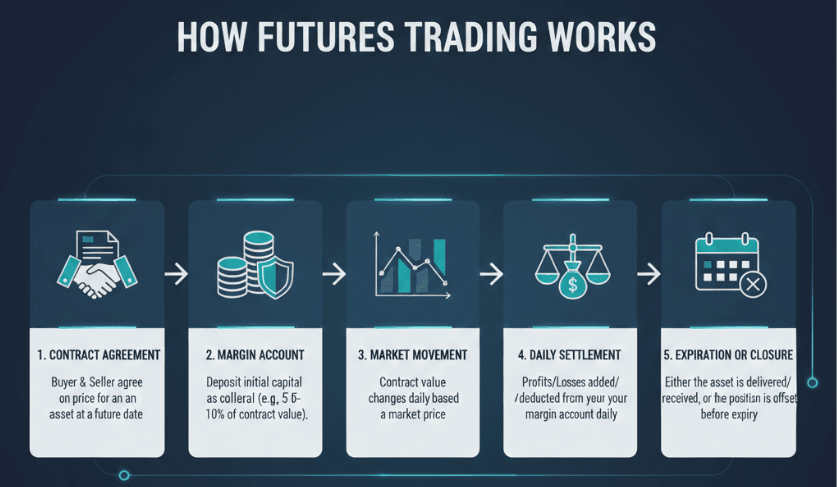
Leverage Opportunities: Traders can control a larger position with a smaller capital investment, potentially increasing returns.
Market Diversity: Futures CFDs cover a wide range of markets, including commodities, indices, and currencies, allowing traders to diversify their portfolios.
Risk Management: Futures can be used to hedge existing positions or portfolios, helping to mitigate potential losses.
Liquidity: The futures markets are typically highly liquid, enabling traders to enter and exit positions with ease.
Accessibility: With online trading platforms like Markets.com, individuals can easily access and trade futures CFDs from anywhere in the world.
While futures CFDs offer numerous advantages, they also come with inherent risks:
High Volatility: Futures markets can be highly volatile, leading to rapid price changes that can result in significant gains or losses.
Margin Calls: Because futures are traded on margin, traders may face margin calls if the market moves against their position, requiring them to deposit additional funds.
Complexity: Futures trading requires a solid understanding of market dynamics and economic factors. New traders may find it challenging to navigate.
Interest and Fees: Depending on the broker, there may be interest charges on leveraged positions, as well as fees related to trading, which can impact overall returns.
Step 1: Choose a Reputable Broker
Selecting the right broker is crucial when starting futures trading. It’s essential to choose a platform that offers comfortable trading conditions, access to various futures contracts, and comprehensive support. Markets.com stands out as an excellent choice for several reasons:
Step 2: Open a Trading Account
Opening an account with Markets.com is straightforward. To get started, you’ll need to provide some basic information, including identification and financial details.
Registration Process: Complete the registration process by providing your details and verifying your identity.
Choose Account Type: Decide whether you want to open a standard account, a margin account, or a demo account for practice.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
Once your account is set up, you will need to deposit funds to start trading. Markets.com offers a variety of funding methods, including credit/debit cards, bank transfers, and e-wallets.
Step 4: Practice with a Demo Account
For those new to futures CFDs, utilizing a demo account is an excellent way to familiarize oneself with the trading platform without risking real money. The demo account simulates market conditions and allows traders to practice their strategies in a risk-free environment.
Step 5: Develop a Trading Strategy
Before placing real trades, it’s essential to develop a clear trading strategy. Consider factors such as:
Market Analysis: Incorporate both fundamental and technical analysis to inform your trading decisions.
Risk Management: Establish a risk management plan that includes stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Trade Size: Determine appropriate trade sizes based on personal risk tolerance and account balance.
Step 6: Start Trading Futures CFDs
After you feel confident in your strategy, you can begin trading real futures CFDs. Monitor your trades regularly and adjust your strategy as needed based on market conditions and personal performance evaluation.

Trading Strategies for Futures CFDs
Adopting effective trading strategies can enhance success in futures trading. Here are several commonly used approaches:
Trend Following
This strategy involves identifying and following market trends, utilizing tools such as moving averages and trend lines. Traders may enter long positions when prices ascend and short positions when prices descend.
Spread Trading
Spread trading refers to simultaneously buying one futures contract while selling another related contract. This strategy aims to capitalize on the price discrepancies between the two contracts, usually within the same commodity or sector.
Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same day. Traders utilizing this method focus on short-term price movements and often use technical analysis tools to inform their decisions.
Swing Trading
Swing trading aims to capture price swings over several days or weeks. Traders may use patterns, indicators, and market analysis to determine entry and exit points.
Hedging
Hedging involves taking positions in futures to mitigate risks associated with adverse price movements in an underlying asset. This can be particularly advantageous for businesses or individuals with exposure to certain commodities.
Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy, where traders hold positions for weeks or months based on fundamental analysis. This approach requires a deep understanding of the market environment and underlying factors influencing the asset.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
Importance of Regulation
Regulations in the futures CFD market serve to protect traders and maintain market integrity. Regulatory bodies oversee trading practices, ensure transparency, and enforce compliance with financial laws.
Key Regulatory Bodies
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC): In the United States, the CFTC regulates futures and options markets, focusing on protecting market participants from fraud, manipulation, and abusive practices.
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): In the UK, the FCA regulates the conduct of financial firms, ensuring that they adhere to high standards of integrity and transparency.
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA): The ESMA oversees securities markets within the European Union, implementing regulations to enhance market stability and investor protection.
Compliance and Best Practices
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards is essential for brokers and traders alike. Best practices include:
Know Your Customer (KYC): Brokers are required to conduct thorough KYC checks to verify the identity of their clients, helping to prevent fraud and money laundering.
Regular Audits: Regulatory bodies may conduct audits of trading platforms to ensure they comply with established standards and practices.
Transparency: Providing clear information about fees, margin requirements, and trading conditions is vital for maintaining trust with clients.
Understanding Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves evaluating historical price movements and volume data to forecast future price action. Traders use various tools and indicators to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry and exit points.
Charts and Patterns: Price charts play a fundamental role in technical analysis. Traders look for specific patterns, such as head and shoulders, flags, and triangles, which can signal potential market movements.
Indicators: Commonly used indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands. These help traders gauge market momentum and volatility.
Utilizing Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating the intrinsic value of an asset based on economic factors, news events, and market conditions. For futures trading, key fundamental factors include:
Supply and Demand Dynamics: Understanding the balance between supply and demand is crucial for predicting price movements in commodities.
Economic Reports: Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates, provide insight into market sentiment and can affect futures prices.
Geopolitical Events: News related to international trade agreements, conflicts, and political instability can impact market dynamics, particularly in commodity markets.
Tips for Successful Futures CFD Trading
To enhance your chances of success in futures CFD trading, consider the following tips:
Continuous Education: Stay informed about market trends, trading strategies, and industry news. Continuous learning is vital for adapting to changing market conditions.
Develop a Trading Plan: A well-defined trading plan outlining your goals, risk tolerance, and strategies will help guide your decisions.
Use Stop-Loss Orders: Implementing stop-loss orders can protect your capital by automatically closing a position if the market moves against you.
Diversify Your Portfolio: Diversifying your futures trading portfolio across various asset classes can reduce risk exposure and enhance potential returns.
Stay Disciplined: Emotional decision-making can lead to mistakes in trading. Maintaining discipline and adhering to your trading plan are vital for long-term success.
Review and Adjust Your Strategy: Regularly assess the effectiveness of your trading strategies. Be prepared to adjust your approach based on market performance and new information.
Futures CFD trading presents lucrative potential for those willing to navigate its complexities. With the added benefits of leverage, liquidity, and accessibility, traders can explore various markets and implement diverse strategies. However, thorough research, education, and risk management remain essential components of achieving favorable outcomes.
For those looking to commence their futures trading journey, Markets.com is a recommended broker, delivering an intuitive platform equipped with educational resources and a broad array of futures contracts. With this guidance, newcomers can confidently step into the dynamic world of futures CFDs and develop their trading ambitions.
In this fast-paced market, staying informed and adapting strategies is crucial. By understanding the nuances of futures trading, individuals can make informed decisions and enhance their engagement in the financial landscape. Whether approaching futures trading as a serious investment or as a hobby, the right tools and knowledge can make all the difference. Markets.com offers a robust platform for traders looking to take advantage of the myriad possibilities within the futures CFD market.
Additional Resources
Recommended Reading
Books on Trading: Look for books that cover trading psychology, risk management strategies, and advanced trading techniques.
Online Courses: Enroll in online courses that offer structured learning about futures trading, technical analysis, and market strategies.
Webinars and Workshops: Participate in webinars and workshops hosted by experienced traders and professionals for actionable insights and interactive learning.
Community Engagement
Forums and Discussion Groups: Engage with trading communities on forums and social media platforms to gain diverse perspectives and insights on market trends.
Follow Influencers and Experts: Keeping up with industry influencers on social media can provide valuable information and timely updates on the futures market.
By leveraging educational resources, actively engaging in trading communities, and utilizing a robust trading platform like Markets.com, traders can build the skills necessary to navigate the exciting world of futures CFD trading successfully.
Looking to trade futures CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.